Internet of Everything
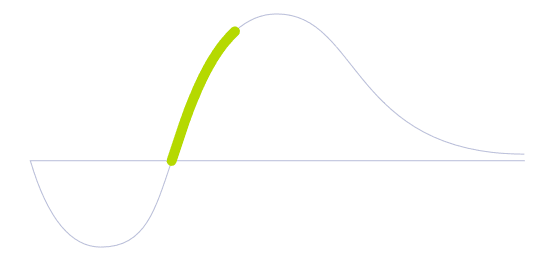
Technology Life Cycle
Marked by a rapid increase in technology adoption and market expansion. Innovations are refined, production costs decrease, and the technology gains widespread acceptance and use.

Technology Readiness Level (TRL)
Experimental analyses are no longer required as multiple component pieces are tested and validated altogether in a lab environment.
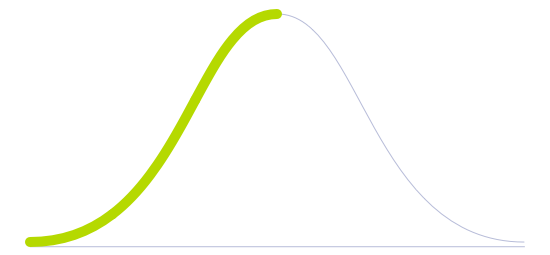
Technology Diffusion
Adopts technologies once they are proven by Early Adopters. They prefer technologies that are well established and reliable.

The Internet of Everything (IoE) represents a significant evolution in connectivity, going beyond the traditional Internet of Things (IoT) to encompass not only devices but also people, processes, and data. This holistic approach aims to solve the increasingly complex challenges of modern urban environments, including efficient resource management, enhancing public safety, and optimising urban mobility. By integrating various components of a city's infrastructure and accelerating technologies such as 5G and Edge Computing, IoE facilitates a smarter, more sustainable approach to urban development and overall connectivity.
At its core, the Internet of Everything combines four key elements: people, data, processes, and things. People are connected through more intuitive and efficient interfaces. Data becomes more valuable through aggregation, analysis, and actionable insights. Processes gain efficiency by adapting to real-time information. Lastly, 'things' refer to the physical devices and sensors interconnected through the internet, from smartphones and wearable technology to home appliances, machinery, facilities, and entire cities. Together, these elements work in unison to automate, enhance, and optimise urban living, making cities more responsive to the needs of their inhabitants.
By enabling the collection and analysis of data from a wide array of sources, urban planners and city councils can make informed decisions that reduce waste, improve energy efficiency, and mitigate environmental impacts, eventually creating Cognitive Twins of entire systems. For instance, smart grids can balance electricity supply and demand in real time, reducing carbon emissions. Smart transportation systems can alleviate traffic congestion, lowering pollution levels and enhancing the quality of urban life. Moreover, the integration of real-time data processing with urban infrastructure supports proactive governance and public services, contributing to more resilient and adaptive urban ecosystems.
Image generated by Envisioning using Midjourney