Machinery as a Service
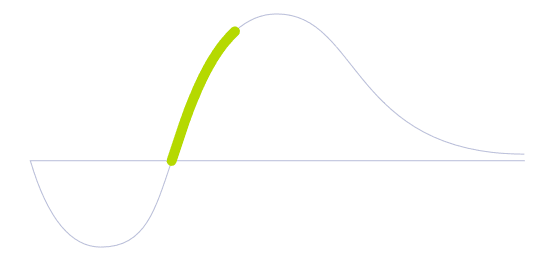
Technology Life Cycle
Marked by a rapid increase in technology adoption and market expansion. Innovations are refined, production costs decrease, and the technology gains widespread acceptance and use.

Technology Readiness Level (TRL)
Prototype is fully demonstrated in operational environment.
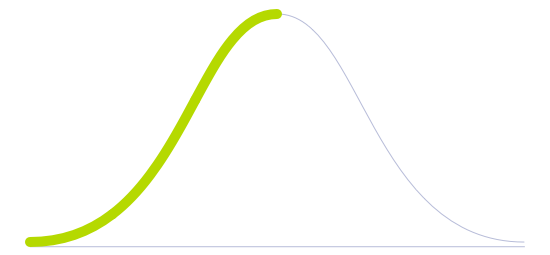
Technology Diffusion
Adopts technologies once they are proven by Early Adopters. They prefer technologies that are well established and reliable.

Machinery as a Service, often referred to as MaaS, addresses the challenges of high initial investment, equipment maintenance, and the need for flexibility in today's manufacturing landscape. MaaS, also known as Equipment-as-a-Service (EaaS), is a subscription-based model where manufacturers can access and utilise machinery and equipment on a pay-as-you-go basis. The underlying technology involves a network of interconnected industrial machines, sensors, and data analytics. In some models, manufacturers can remotely monitor, control, and optimise their production processes through a secure online platform.
This solution significantly reduces the upfront costs associated with purchasing and maintaining machinery, allowing companies to allocate capital more efficiently and democratising access to smaller players who could not invest in advanced machinery. It also promotes agility, enabling manufacturers to quickly adapt to changing market demands and product variations without the burden of owning and managing a diverse set of equipment. Additionally, MaaS fosters a sustainable approach to manufacturing, as more companies can access cutting-edge, energy-efficient machinery, possibly reducing the environmental footprint of outdated equipment.
Future Perspectives
With the increasing adaptation of this model, future factory floors would not be inhabited by humans. Machinery will be programmed, operated, and monitored entirely remotely, with co-bots helping manage the handling and taking of the products from the factory floor to the logistic chain.
In the future, with the wide spread of highly customized products, especially in the case of markets with hyper-personalized customer needs, such as the beauty and cosmetics industry, having dynamic, automated, and scalable production of goods tracked with blockchain from the factory floor to the door of each consumer holds great potential to improve current business approaches.
Image generated by Envisioning using Midjourney